The Affordable Care Act’s (ACA) future continues to be uncertain as the law’s constitutionality will once again be considered by the U.S. Supreme Court in California v. Texas 1 (known as Texas v. U.S. in the lower courts). Oral argument is scheduled for Tuesday, November 10, 2020. This ongoing litigation challenges the ACA’s minimum essential coverage provision (known as the individual mandate) and raises questions about the entire law’s survival. The individual mandate provides that most people must maintain a minimum level of health insurance coverage; those who do not do so must pay a financial penalty (known as the shared responsibility payment) to the IRS. The individual mandate was upheld as a constitutional exercise of Congress’ taxing power by a five member majority of the Supreme Court in NFIB v. Sebelius in 2012.
In the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), Congress set the shared responsibility payment at zero dollars as of January 1, 2019, leading to the current litigation. In December 2019, the U.S. Court of Appeals for the 5 th Circuit affirmed the trial court’s decision that the individual mandate is no longer constitutional because the associated financial penalty no longer “produces at least some revenue” for the federal government. 2 But, instead of deciding whether the rest of the ACA must be struck down, the 5 th Circuit sent the case back to the trial court for additional analysis. However, the Supreme Court has now agreed to review the case.
The ACA remains in effect while the litigation is pending. However, if all or most of the law ultimately is struck down, it will have complex and far-reaching consequences for the nation’s health care system, affecting nearly everyone in some way. A host of ACA provisions could be eliminated, including protections for people with pre-existing conditions, subsidies to make individual health insurance more affordable, expanded eligibility for Medicaid, coverage of young adults up to age 26 under their parents’ insurance policies, coverage of preventive care with no patient cost-sharing, closing of the doughnut hole under Medicare’s drug benefit, and a series of tax increases to fund these initiatives.
This issue brief answers key questions about the litigation as we await a decision from the Supreme Court about the ACA’s survival.
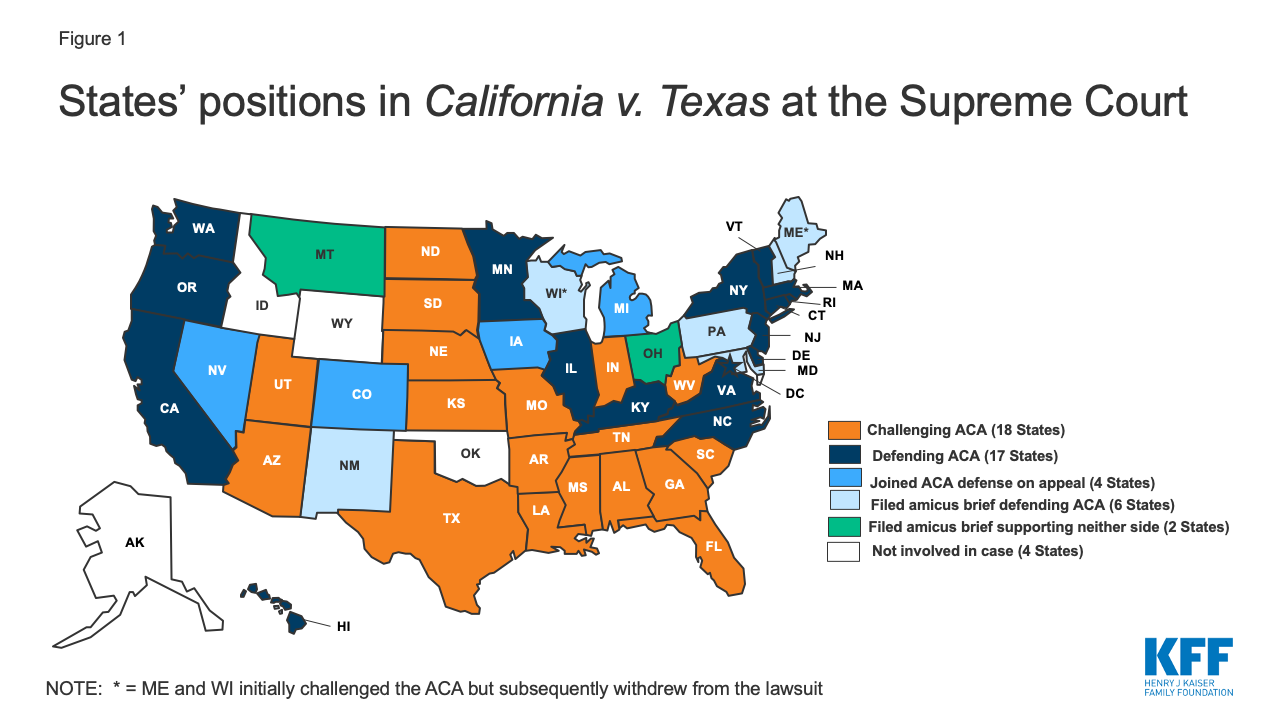
A group of 20 states, led by Texas, sued the federal government in February 2018, seeking to have the entire ACA struck down (the “state plaintiffs”). 3 These states are represented by 18 Republican attorneys general and 2 Republican governors. After Democratic victories in the 2018 mid-term elections, two of these states, Wisconsin and Maine, withdrew from the case in early 2019, leaving 18 states challenging the ACA on appeal (Figure 1). 4

Figure 1: States’ positions in California v. Texas at the Supreme Court
Two individuals joined the lawsuit in the trial court in April 2018, as plaintiffs challenging the ACA. 5 These plaintiffs are self-employed residents of Texas who claim that the individual mandate requires them to purchase health insurance that they otherwise would not buy, although there is no penalty if they fail to buy coverage.
Throughout the litigation, the federal government has not defended the constitutionality of the ACA’s individual mandate. Instead, the federal government agrees with the state and individual plaintiffs that the individual mandate is no longer constitutional under Congress’s taxing power as a result of the TCJA provision that set the financial penalty at zero. 6 It is unusual for the federal government to take a position that does not seek to uphold a federal law.
Unlike the plaintiffs, the federal government argued at the trial court that only the ACA’s protections for people with pre-existing conditions, including guaranteed issue and community rating, should be struck down along with the individual mandate. The federal government took the position that these provisions cannot function effectively without the individual mandate but the rest of the ACA should be allowed to survive.
Notably, the federal government changed its position while the case was on appeal at the 5 th Circuit (Figure 2). First, the federal government took what the 5 th Circuit called a “significant change in litigation position” 7 by deciding to support the trial court’s decision that the individual mandate is inseverable from the entire ACA. 8 This change came after the federal government had appealed, asking the 5 th Circuit to review the trial court’s decision. Next, the federal government raised new arguments about the scope of relief that the court should grant, asserting that the federal government should be enjoined from enforcing only the ACA provisions that injure the plaintiffs. For example, the federal government identified “several criminal statutes used to prosecute individuals who defraud our healthcare system” that are part of the ACA that it believes should survive. 9 The federal government also argued for the first time in the 5 th Circuit that any injunction prohibiting enforcement of the ACA should apply only in the plaintiff states. 10
The federal government is asking the Supreme Court to prohibit it from enforcing only the ACA provisions that are found to harm the individual plaintiffs. Even though the federal government is arguing that the entire ACA should be found invalid (because the individual mandate is no longer constitutional and cannot be severed from the rest of the law), the federal government does not want the Court to necessarily prevent it from still enforcing parts of the law. Instead, the federal government is seeking a more limited remedy: it contends that “relief should reach only the enforcement of the ACA provisions that injure the individual plaintiffs.” 11 The federal government has not clearly identified which specific ACA provisions fall into this category and is asking the Supreme Court to send the case back to the lower courts to determine this issue. 12
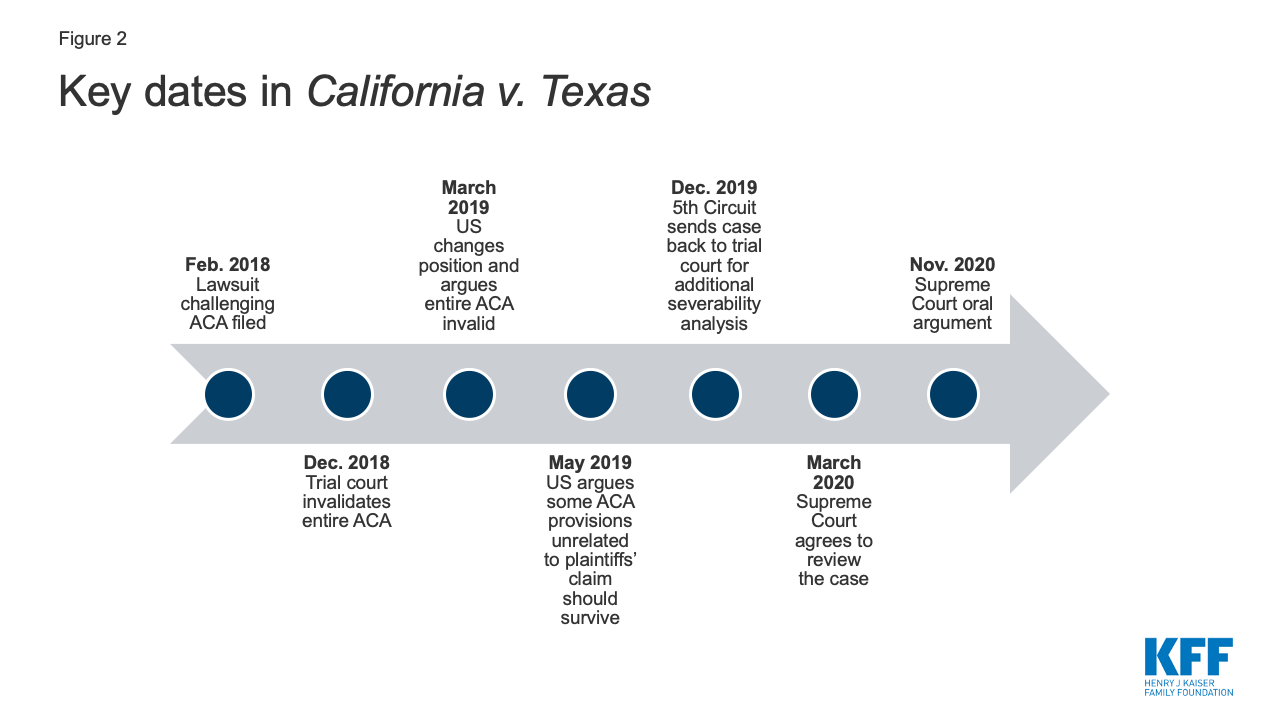
Figure 2: Key dates in California v. Texas
Another 17 states, led by California, were permitted by the trial court to intervene in the case and defend the ACA (the “state intervener-defendants”). Subsequently, the 5 th Circuit allowed four more states to intervene in the case on appeal, bringing the total number of states defending the ACA in the case to 21 . 13 In addition, six states filed an amicus brief in the Supreme Court in support of the ACA (Figure 1).
The 5 th Circuit also allowed the U.S. House of Representatives to intervene in the case to defend the ACA on appeal. 14 However, the 5 th Circuit did not decide whether the House has standing to pursue the appeal. 15 The standing of the state intervener-defendants and/or the House is particularly important in this case, since the federal government is not defending the ACA (Figure 3). At the Supreme Court, the parties are not contesting, and the Court has not asked for briefing on, California’s ability to pursue an appeal (California and the House both filed cert petitions raising the same issues, and the Court accepted California’s petition).
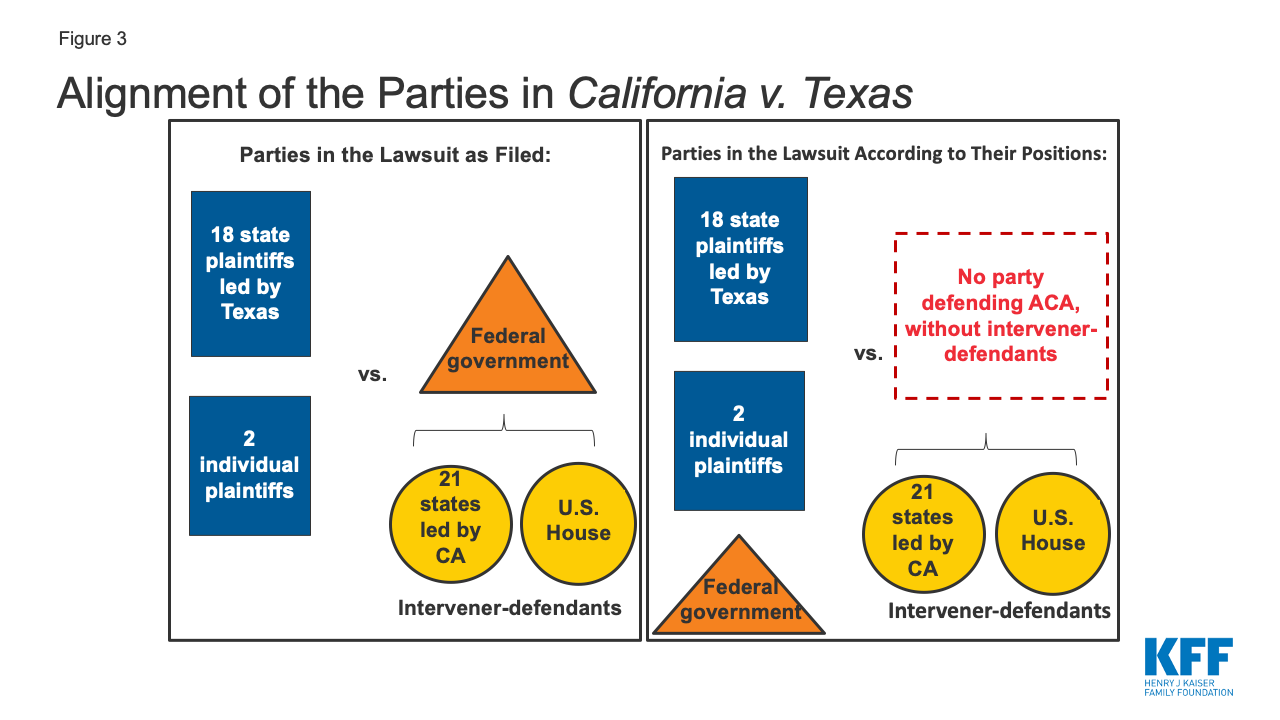
Figure 3: Alignment of the Parties in California v. Texas
The 5 th Circuit issued a 2:1 decision finding the individual mandate unconstitutional and sending the case back to the trial court for additional analysis about whether the rest of the ACA can survive. There are three main issues in the case: (A) whether the parties have standing to invoke the court’s jurisdiction; (B) whether the ACA’s individual mandate, as amended by the TCJA, is constitutional; and (C) if the mandate is unconstitutional, whether it can be severed from the rest of the ACA, or on the other hand, whether other provisions of the ACA also must be invalidated. Figure 4 illustrates the legal questions and potential outcomes in the case.
The 5 th Circuit decided that the case presented a live controversy for it to resolve, despite the unusual alignment of the parties’ positions. Although the federal government is “in almost complete agreement on the merits of the case” with the plaintiffs, it also has indicated that it will continue to enforce the ACA unless or until a court issues a final order striking the law down. 16 The state intervener-defendants have standing to pursue an appeal because they would be injured by the loss of federal ACA funding, such as funding for the Medicaid expansion and the Medicaid Community First Choice attendant care program, if the trial court’s decision is upheld. 17
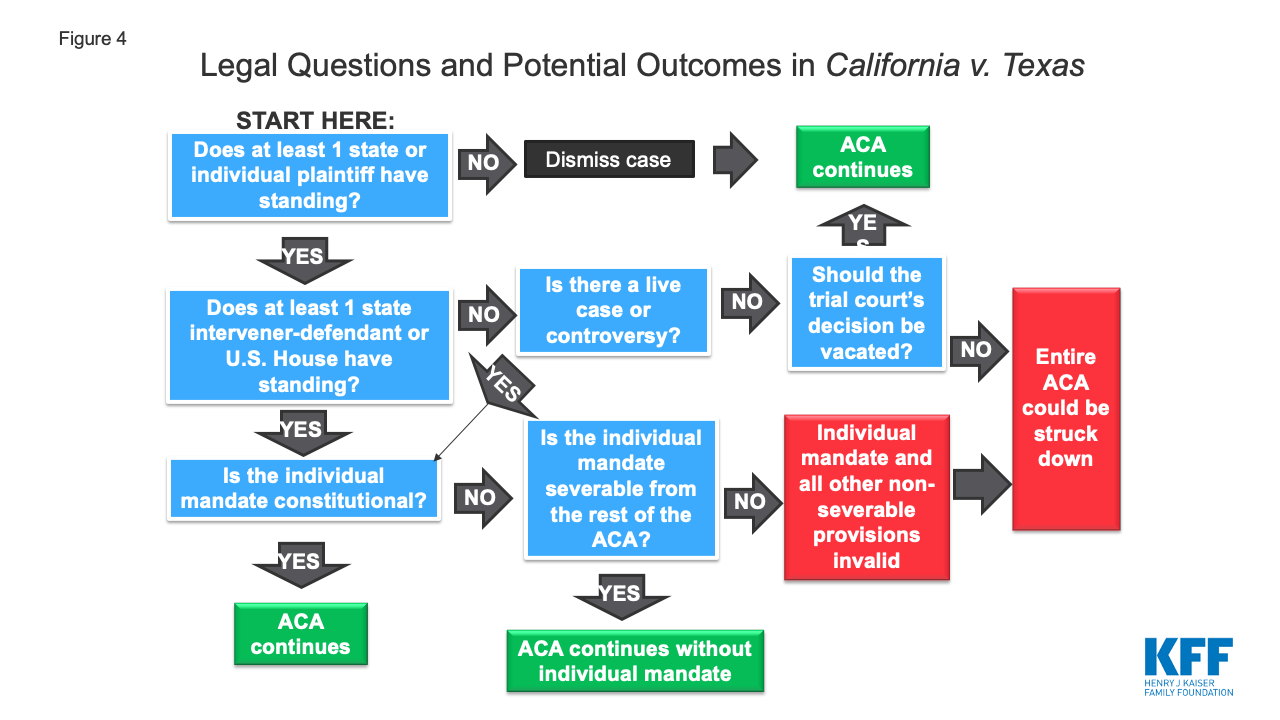
Figure 4: Legal Questions and Potential Outcomes in California v. Texas
The 5 th Circuit decided that the both the individual and state plaintiffs have standing to challenge the ACA in court. Standing ensures that federal courts are deciding actual cases or controversies as required by the U.S. Constitution. Standing is essential for the court to have jurisdiction to decide a case and therefore cannot be waived. To establish standing, a party must suffer an injury that is concrete and actual or imminent; fairly traceable to the challenged conduct; and likely to be redressed by a favorable court ruling. The 5 th Circuit agreed with the trial court that the individual plaintiffs have standing because they have spent money that they otherwise would not have spent, absent the individual mandate, to purchase health insurance. 18 The 5 th Circuit also decided that the state plaintiffs have standing because they are incurring costs from the individual mandate from having to verify which state employees have minimum essential coverage. 19
The dissent reached the opposite conclusion, finding that neither the individual nor the state plaintiffs has standing to bring the case. According to the dissent, any injury experienced by the individual plaintiffs “is entirely self-inflicted” because “absolutely nothing” will happen to them if they do not purchase insurance to meet the individual mandate now that the penalty is set at zero. 20 The dissent also concluded that the state plaintiffs lack standing because they failed to provide evidence showing that “at least some state employees have enrolled in employer-sponsored health insurance” or that “anyone has enrolled in their Medicaid programs solely because of the unenforceable coverage requirement.” 21
The 5 th Circuit decided that the individual mandate as amended by the TCJA is unconstitutional. The court agreed with the state and individual plaintiffs and the federal government’s assertion that the requirement to produce some revenue is “essential” to the Supreme Court’s earlier finding in NFIB that the individual mandate could be saved as a valid exercise of Congress’s power to tax. 22 Without that feature, the mandate is a command to purchase health insurance, which as the Supreme Court held in NFIB, is an unconstitutional exercise of Congress’ power to regulate interstate commerce.
The dissent concluded that the individual mandate remains constitutional because the TCJA amendment is “a law that does nothing.” 23 The dissent reasoned that the TCJA did not change the text of the coverage requirement and therefore did not change the individual mandate into a mandatory command to purchase insurance. Rather, Congress “changed the parameters” of the choice about whether to purchase insurance from paying a tax penalty to “no consequences at all.” 24
The 5 th Circuit sent the case back to the trial court for additional analysis about which ACA provisions should survive without the individual mandate. The trial court incorrectly focused on the intent of Congress in 2010 when passing the ACA and instead should have considered Congress’ intent when enacting the TCJA and setting the shared responsibility payment at zero in 2017. 25 In so doing, the trial court should “employ a finer-toothed comb. . . and conduct a more searching inquiry into which provisions of the ACA Congress intended to be inseverable from the individual mandate. . . us[ing] its best judgment to determine how best to break the ACA down into constituent groups, segments, or provisions to be analyzed.” 26
The 5 th Circuit also directed the trial court to consider the federal government’s new argument that any order prohibiting enforcement of the ACA should extend only to provisions that injure the plaintiffs and apply only in the plaintiff states. The trial court may consider whether the federal government timely raised this argument and whether Supreme Court precedent supports limiting the remedy in this way. 27
The dissent criticized the majority’s failure to send the case back to the trial court instead of resolving the severability issue. Severability is a question of law, which the 5 th Circuit could have resolved without sending the case back to the trial court. The dissent agreed with the majority that the severability analysis should look to the intent of Congress when passing the TCJA in 2017. However, the dissent concluded that the fact that Congress changed the tax penalty amount to zero while leaving the rest of the ACA in place indicates that Congress intended for all of the other provisions to remain in effect. 28
The Supreme Court has agreed to review four legal questions in the case. First, the Court will consider whether Texas and the individual plaintiffs have standing to bring the lawsuit to challenge the individual mandate. If so, the Court will determine whether the TCJA rendered the individual mandate unconstitutional. If the mandate is unconstitutional, the Court will decide whether the rest of the ACA can survive. Finally, if the entire ACA is held invalid, the Court will resolve whether the entire law should be unenforceable nationwide or whether it should be unenforceable only to the extent that provisions injure the individual plaintiffs.
The case will be argued at the Supreme Court on November 10, 2020. The Court has allotted one hour and twenty minutes for oral argument, with 40 minutes for each side. California will argue for 30 minutes of the time allotted to the parties defending the ACA, with the remaining 10 minutes argued by the House. The time allotted to the parties challenging the ACA will be evenly divided between the federal government and Texas, with 20 minutes for each. The Court denied Ohio and Montana’s motion to participate in oral argument as amici curiae in support of neither side. The decision could come as late as the end of term in June 2021.
If the Supreme Court finds that the individual mandate is unconstitutional and invalidates only that provision, the practical result will be essentially the same as the ACA exists today, without an enforceable mandate. If the Supreme Court adopts the position that the federal government took during the trial court proceedings and invalidates the individual mandate as well as the protections for people with pre-existing conditions, then federal funding for premium subsidies and the Medicaid expansion would stand, and it would be up to states whether to reinstate the insurance protections. The Supreme Court also could decide that Texas and the individual plaintiffs do not have standing to bring the lawsuit, which would allow the ACA as it exists today to remain in effect.
The most far-reaching consequences, affecting nearly every American in some way, will occur if the Supreme Court ultimately decides that all or most of the ACA must be overturned, as the federal government now argues. The number of non-elderly individuals who are uninsured decreased by 18.6 million from 2010 to 2018, as the ACA went into effect. The ACA made significant changes to the individual insurance market, including requiring protections for people with pre-existing conditions, creating insurance marketplaces, and authorizing premium subsidies for people with low and modest incomes. The ACA also made other sweeping changes throughout the health care system including expanding Medicaid eligibility for low-income adults; requiring private insurance, Medicare, and Medicaid expansion coverage of preventive services with no patient cost sharing; phasing out the Medicare prescription drug doughnut hole coverage gap; reducing the growth of Medicare payments to health care providers and insurers; establishing new national initiatives to promote public health, care quality, and delivery system reforms; and authorizing a variety of tax increases to finance these changes. All of these provisions could be overturned if all or most of the ACA is struck down by the courts, and it would be enormously complex to disentangle these provisions from the overall health care system.
For now, the ACA remains in effect. The trial court’s original decision that the entire ACA should be invalidated was never implemented and was set aside by the 5 th Circuit. Additionally, the Trump Administration has indicated that it intends to continue enforcing the ACA while the appeal is pending. Although the Supreme Court’s decision in the case could come as late as June 2021, the Court’s decision to review the case now, without waiting for the lower courts to complete their review, will minimize the amount of time that the ACA’s future remains uncertain. 29 If the Supreme Court had not agreed to review the case now, the litigation likely would have continued for several more years, while the trial court issued a new decision on severability and that decision was then reviewed by the 5 th Circuit, before returning to the Supreme Court. Still, 10 years after its enactment, the only certainty for the ACA in the foreseeable future is that there is continuing uncertainty about its ultimate survival.